Heart and Lung Transplant National Recovery Program
LOCATION ADDRESS :
14286 Beach Blvd STE 19, Jacksonville Beach, FL 32250
Perfusion & Preservation
Perfusion and Preservation
The successful preservation and perfusion of harvested heart and lungs is critical in order to ultimately use them for transplantation purposes. There are various types of preservation solutions and techniques available for this task, and it is essential to understand the benefits and drawbacks of each. There are two main methods used for preservation: static and dynamic. Static perfusion does not involve flow of fluid through the vessels, while dynamic perfusion involves the circulation of preservation solution through the organ’s vasculature. Dynamic perfusion has been reported to offer superior preservation of organs, as it allows for better oxygenation and nutrient delivery.
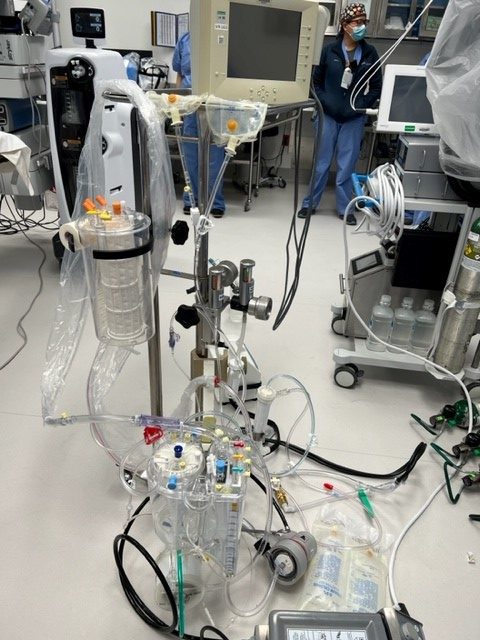
Preservation of lungs:
Lungs require preservation to maintain their ability to exchange gases effectively. The most common method used for lung preservation is cold perfusion with a solution called preservation solution. This solution maintains the pH level of the lung tissues and contains nutrients and electrolytes to support the lung function. During preservation, lungs are cooled to a specific temperature, which helps in reducing the metabolism of lung tissues and minimizing damage due to hypoxia. One of the major challenges of this preservation process is that lungs are highly susceptible to getting waterlogged during the preservation process.
Preservation of Hearts:
The main goal of heart preservation is to prevent damage to heart tissues. The process commonly used for heart preservation is called cold storage or hypothermic perfusion. During this process, the heart is placed in a sterile container filled with a specialized preservation solution and then cooled to a specific temperature. The preservation solution contains nutrients and electrolytes to maintain heart function, as well as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents to reduce tissue damage. One of the significant challenges in heart preservation is that it requires a well-timed preservation process between the organ harvesting and transplant surgery.
1. Hypothermic Preservation:
This is the most commonly used technique for preserving the harvested heart and lungs. It involves cooling the organs to a temperature of 4-8°C using a preservation solution. This slows down the metabolic rate of the organs and reduces the damage caused by lack of oxygen during the harvesting process
2. Machine Perfusion:
This technique involves connecting the harvested heart or lungs to a machine that delivers oxygenated blood, electrolytes, and nutrients to the organs. It allows the organs to continue functioning and reduces the damage caused by lack of blood flow during the harvesting process.
3. Organ-specific Preservation Solutions:
Specialized preservation solutions. These solutions provide optimal conditions for preserving the organs for transplantation.
4. Normothermic Preservation:
5. Controlled Oxygenated Rewarming:
This technique involves gradually bringing the organs back to body temperature with the use of a specialized machine. It allows the organs to regain function and can reduce the risk of complications during the transplantation surgery.
It is important to note that the choice of preservation technique depends on the specific circumstances of the organ transplant, and the decision should be made by the transplant team in consultation with the organ donor’s.
We have most of the preservation and perfusion solutions
We have highly trained preservationists
We have dedicated trained NRP Perfusionist
We have dedicated trained OCS perfusionist for heart and lungs
We educate and train individuals in our program
We help transplant centers to achieve their goal
